Filter
246
Featured
217
7
Topics
65
48
34
27
26
19
16
15
14
13
12
7
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Language
Document type
39
8
7
3
2
2
2
1
1
1
Countries / Regions
Authors & Publishers
Media focus
Publication Years
Methods applied
Journals
Output Type
"This Information Ecosystem Assessment documents how information around the COVID-19 pandemic is produced, consumed, and shared in Sudan contributing to the existence of multiple and overlapping information sub-systems within the supply side of the broader ecosystem. The findings show how the centra
...
„Quelle: Internet“? Digitale Nachrichten- und Informationskompetenzen der deutschen Bevölkerung im Test
Berlin: Stiftung Neue Verantwortung (2021), 143 pp.
"Eine Auswahl der Test-Ergebnisse im Überblick:
1) Unterschiede zwischen Desinformation, Information, Werbung und Meinung wer den zum Teil nur schwer erkannt [...]
2) Ob eine Quelle vertrauenswürdig ist, wird oft richtig eingeschätzt. Interessens konflikte werden seltener erkannt [...]
3) Kennzei
...
Liberians Want a Free Media – Within Limits – and Unrestricted Access to Social Media
Afrobarometer (2021), 12 pp.
"Radio is the dominant news source in Liberia, tuned in “every day” or “a few times a week” by 87% of adults. Almost four in 10 citizens (38%) say they regularly get news from the Internet and social media, while only about one in five are regular consumers of news via television (21%) and n
...
Ugandans See Social Media as Beneficial and Want Unrestricted Access, But Are Wary of its Use to Spread Fake News
Afrobarometer (2021), 11 pp.
"Daily news consumption via social media (11%) and the Internet (9%) has doubled in Uganda since 2015, though these platforms still lag far behind television (27%) and radio (54%) as daily news sources. Six in 10 Ugandans (60%) say they are aware of social media. Awareness is less widespread among w
...
Shaped by Trauma, History and Hope: Audiences’ Perceptions of Social Cohesion Coverage in Ninewah, Iraq
Media in Cooperation and Transition (MiCT) (2021), 41 pp.
"This research analysis aims to assess perceptions of media coverage of social cohesion in Ninewah and understand how content is consumed and assessed by audiences in the province. What this report has demonstrated is that while there is a distrust of the media at a national level, local media are p
...
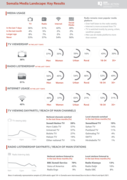
Somalia Media Landscape: Key Results
London: BBC Media Action (2021), 1 p.
"Radio remains most popular media platform. Over half listen to the radio weekly. Internet is more accessed than TV. TV is watched mostly by young, urban, wealthier people. Men use all media platforms more than women [...] A nationally representative sample of 2,004 adults aged 18+ in Somalia were i
...
Turkey's Changing Media Landscape
Washington, DC: Center for American Progress (2020), 24 pp.
"This report highlights numerous troubling developments in Turkey’s media landscape. Distrust in the media has reached crisis proportions, with fully 70 percent of Turks viewing the media as dishonest. These doubts have formed the backdrop for rapid shifts in how Turks access political news and in
...
Information Needs Assessment of the City of El Alto (Bolivia)
La Paz: Fundación UNIR; Internews (2020), 61 pp.
"There are close to 60 operating print news media, radio and television stations in El Alto, in addition to a half dozen digital information portals. There are approximately 200 journalists in El Alto, but most of them lack formal labor contracts and perform their work as independent producers or co
...
El futuro de los medios
cadem (2020), 27 slides
Sri Lanka Media Audience Study 2019: Consuming News in Turbulent Times
International Media Support (IMS) (2020), 63 pp.
"Across various demographics, Sri Lankan audiences highly value news and current information. More than three quarters (77%) identified news as being very important, and another 18% said it was somewhat important. National news on current affairs had the highest level of audience interest (76%), fol
...
Face à l’hégémonie de la télévision et la radio, l’Internet et les médias sociaux continuent leur popularité grandissante en Côte d’Ivoire
Afrobarometer (2020), 11 pp.
"L’utilisation de la mesure d’audience par les médias est faible en Côte d’Ivoire. Selon une étude du Ministère de la Communication, de l’Économie Numérique et de la Poste (2017), la plupart des médias ivoiriens naviguent à vue sans une véritable connaissance et maîtrise du marché
...
La pauvreté dans le monde & les enjeux de développement: La consommation des médias en France
Development Engagement LAB (2020), 93 slides
"C’est par le biais des actualités portant sur les questions migratoires et les conflits armés que les Français sont le plus à même de s’informer à propos de la pauvreté dans le monde. Le public français préfère être informé sur la pauvreté dans le monde à l’occasion des actualit
...
Media Consumption Report: Platforms and Tools for Reaching and Engaging Urban and Rural Youth
Washington, DC: USAID Cambodia Green Future Activity (2020), iii, 22 pp.
"This report provides an overview of media consumption from the perspectives of selected media practitioners in Cambodia and highlights some of the key communication tools, products, materials, and platforms they have used to reach their respective target audiences. This report maps trends across bo
...
Estudio: Medios de comunicación en coronavirus
Santiago de Chile: cadem (2020), 34 slides
"Independent media outlets in the Western Balkans are facing major challenges to their financial sustainability. With the exception of some of the largest broadcasters with national coverage and the most visited online media, the majority of media outlets across the region are not sustainable busine
...
Port-Au-Prince Information Ecosystem Assessment
Internews; Panos Caribbean (2020), 70 pp.
"Key finding 1: A trusted thirdperson is the most important information provider. When asked for their main source of information, family, friends, and religious leaders accounted for 89% of the response choices combined. Additionally, 97% stated they trust their family and friends. Key finding 2: S
...
News Media Trust and its Impact on Media Use: Toward a Framework for Future Research
Annals of the International Communication Association, volume 44, issue 2 (2020), pp. 139-156
"In contemporary high-choice media environments, the issue of media trust and its impact on people’s media use has taken on new importance. At the same time, the extent to which people trust the news media and how much it matters for their use of different types of media is not clear. To lay the g
...
Poursuite des cours par télévision, radio, et Internet pendant la pandémie du COVID-19: Atouts et contraintes au Togo
Afrobarometer (2020), 10 pp.
"Quatre Togolais sur cinq environ disposent d’une radio dans leur ménage (81%) et suivent régulièrement les informations à la radio (78%). Deux ménages sur cinq (44%) ne possèdent pas de télévision. La moitié (51%) des Togolais ne suivent jamais ou rarement les informations à la télé.
...