Filter
704
Featured
Free Access
395
Key Guidance
3
Top Insights
54
Topics
Media Freedom, Press Freedom
80
Media Landscapes, Media Systems, Media Situation in General
74
Media Law & Regulation
68
Journalism Education & Training
28
Digital & Social Media Use, Internet Use
25
Digital Media Censorship, Control & Filtering, Internet & Social Media Censorship
23
Censorship
23
Disinformation, Misinformation, Fake News
23
Media Assistance
23
Press Freedom & Communication Rights Violations
21
Trust in the Media, Credibility of Media
20
Associations & Networks of Journalists
20
Politics and Media
19
Media Management
18
Migration & Refugees Reporting & (Social) Media Representation
18
Digital Activism, Cyber Advocacy
17
Journalistic Quality
16
Access to Internet & Digital Communications
15
Media Use, Media Consumption
15
Media / Communication Control
15
Safety of Journalists, Safety Risks of Media Workers
15
Media & Communication Policies
15
Islam and Communication
15
Female Journalists & Media Workers
14
Journalism
14
Press Landscapes
14
Democracy / Democratization and Media
14
Audiences & Users
13
Freedom of Expression
12
Social Media
12
Ethnic Media, Minority Media
12
Diversity & Pluralism in Media / Communication
12
Post-Socialist Media Systems & Landscapes
12
Public Service Broadcasting
12
Digital Divide, Digital Inequalities
11
Media Markets
11
Authoritarian Regimes: Government Communication Strategies
10
Cybersecurity, Digital Safety, Privacy, Right to Privacy
10
Government Communication Strategies
10
Hate Speech, Hate Speech in Social Media
10
Online News
10
ICT Regulation
10
News Agencies
10
Television
10
Media Use: Migrants & Diasporas
9
Conflict Reporting, Armed Conflict Reporting
9
Internet
9
Soap Operas & Telenovelas
9
Self-Regulation of Media
9
Media Capture, Vested Political & Other Interests in the Media
9
Propaganda
9
Public Media, State Media
9
Access to Public Information, Freedom of Information, Right to Information
8
Surveillance, Surveillance Technologies, Spyware
8
Public Diplomacy, Cultural Diplomacy
8
Digital Journalism, Online Journalism
8
Media Concentration
8
Media Ownership
8
Islam: Media Representation & Reporting
8
Radio Landscapes
8
Television Landscapes
8
Public Spheres
8
Radio
8
Mobile Phone Use
7
Authoritarian Regimes: Media Systems & Landscapes
7
Self-Censorship
7
Participatory Communication
7
Collective Memory: Violent Conflicts & Wars
7
Digital Platforms & Intermediaries
7
ICT Industries & Markets
7
Ethnic Television, Minority Television
7
Conspiracy Narratives, Conspiracy Theories
7
Countering Hate Speech, Disinformation & Propaganda
7
Political Economy of Media
7
Environmental Journalism
7
Ethics in Media & Communication
7
Journalism Ethics
7
Gender and Media, Gender and Communication
7
Russia: Foreign Information Operations, International Broadcasting, Public Diplomacy
7
Human Rights Violations
7
Freedom of Expression Online, Internet Freedom
6
Harassment & Intimidation of Journalists
6
State Influence on the Media
6
Extremism & Terrorism Reporting
6
Extremist & Terrorist Digital / Social Media Presence
6
Media Assistance Projects & Programs: Case Studies
6
Development Communication, Communication for Development (C4D)
6
Social Media in Political Communication
6
Twitter & Microblogs
6
Economics of Media
6
International Communication
6
Foreign News, International News
6
Transnational Broadcasting, International Broadcasting
6
Media & Information Literacy
6
Media Outlets, Media Associations
6
Newspapers
6
Telecommunication Infrastructure
6
Access to Information Laws, Right to Information Regulation
5
Advertising
5
Advertising Markets & Industries
5
Gender Advocacy & Empowerment, Gender Mainstreaming
5
Comics, Cartoons, Caricatures
5
Communication Rights
5
Violence Against Journalists & Media Personnel
5
Alternative Communication & Media
5
Community Radios
5
Collective Memory & Media, Media Representation of History
5
Social Change & Media / Communication
5
Financing Digital / Online Media
5
Democratization & Digital Media / Social Media
5
Facebook
5
Mobile Phone Markets
5
Romani People
5
Media Industries
5
Economy
5
Television Entertainment, Television Entertainment Programmes
5
Defamation of Religion (Blasphemy)
5
Good Practice Examples
5
HIV / AIDS Communication
5
History of the Press
5
Media Development Indicators
5
Religious Freedom
5
Politics
5
Populism
5
National Identity & Media, Nationalism & Communication
5
Political Transition and Media
5
Islamist Communications & Media
5
Corruption & Combating Corruption
5
Area & Regional Studies
4
Digital & Social Media Use: Youth
4
Media & ICT Use in Authoritarian Regimes / Dictatorships
4
Television Consumption, Televison Use, Television Audiences
4
Independent & Oppositional Media in Authoritarian Regimes
4
Book Markets & Industries
4
Election Campaigns
4
Christian Minorities
4
Persecution of / Violence Against Christians
4
Documentaries, Television Documentaries, Web Documentaries
4
National Cinemas, National Film Production
4
Exile Journalism, Exile Media
4
Genocides
4
Russia-Ukraine War <2014-
4
Conflict Prevention, Mediation & Reconciliation: Role of Media
4
Conflict-Sensitive & Peace Journalism
4
Extremist & Terrorist Communication Strategies and Media
4
Foreign Conflict Reporting, International War Reporting
4
War Reporting
4
Behaviour Change Communication
4
Edutainment Television Programmes
4
Data Journalism, Computer-Assisted Investigative Reporting
4
Digital Media Landscapes
4
Digital & Information Literacy
4
E-Governance, E-Democracy
4
Digitalisation, Online Communication & Democracy / Democratization
4
Disaster & Humanitarian Crisis Communication
4
Poverty & Poverty Reduction
4
Codes of Journalistic Ethics
4
Press Councils
4
COVID-19 Communication
4
European Union (EU)
4
Investigative Journalism
4
Media Assistance: Journalism Education & Training
4
Journalists Dealing with Risks & Threats, Resilience & Wellbeing of Media Workers
4
Journalists: Professional Identity & Values
4
Election Reporting
4
Protests, Protest Movements, Protest Reporting & Media Representation
4
Religion: Media Representation
4
Working Conditions of Journalists & Media Personnel
4
COVID-19 Pandemic: Effects on Journalism, Media & Communication
4
Media, Mass Media
4
Internet Governance, Internet Policies
4
Public Service Broadcasting: Regulation & Governance
4
Financing Media, Financial Media Management
4
Migrants, Refugees, Diasporas & Media
4
Diasporas
4
Civic Engagement, Citizen & Community Participation
4
Magazines
4
Youth Radio Programmes, Youth Radio Stations, School Radios
4
Society
4
Inequalities
4
Telecommunications
4
Television Channels
4
Al-Jazeera
4
Non-Western Communication Approaches
4
Government Advertising, State Advertising
3
Civic Engagement, Citizen Participation, Civil Society & Digital Communication
3
Social Movements: Communication Strategies & Practices
3
Agricultural Information & Extension
3
Media Use: Minorities & Disadvantaged Groups
3
Media Use: Youth
3
News Consumption & Information Sources of Media Users
3
Authoritarian Regimes, Dictatorships
3
Children's Books & Literature
3
Campaigning: Experiences
3
Church History
3
Cinema
3
Asian Cinema
3
Films
3
Television Programme & Format Trade
3
Impunity for Crimes Against Journalists & Media Personnel
3
Community Media
3
Participatory Videos & Community Filmmaking
3
Storytelling
3
Conflict Areas: Media Systems, Media Landscapes, Role of Media
3
Information Warfare, Psychological Warfare
3
Media Assistance in Conflict Regions & Fragile Countries
3
Media Ethnography
3
Collective Identities & Media
3
Democracy Assistance
3
Communicating Development Projects, Media in Development Programmes
3
Communication for Social Change
3
Development and Media
3
Edutainment Health Programmes
3
Internet / Social Media Law & Regulation
3
Digital Political Communication
3
Internet Markets
3
Digital Media Markets
3
Digital Economies, Digital Societies
3
Ecological Footprint & Sustainability of Digitalization, E-Waste & Recycling
3
Economic Development: Role of ICTs & Media
3
Disadvantaged Groups & Communication, Minorities & Media
3
Integration of Minorities: Role of Media
3
LGBT & Communication / Media
3
Minorities & Disadvantaged Groups: Reporting & Media Representation
3
Earthquakes, Floods, Tsunamis, Natural Disasters
3
Foreign Disinformation, Foreign Information Manipulation Operations, Foreign Propaganda
3
Archives
3
Television Markets
3
Media Viability & Financial Sustainability
3
Education and Communication / Media
3
Political Parody and Satire
3
Accountability & Transparency of the Media
3
Defamation Law & Regulation
3
Fact-Checking & Verification of Sources
3
Feminism & Communication
3
Gender-Based Harassment, Intimidation & Violence
3
Gender-Based Harassment, Intimidation & Violence: Media Representation & Reporting
3
Gender Relations
3
History of Media & Communication
3
History of Communication: Islam
3
Intercultural Communication, Intercultural Competencies
3
Foreign Correspondents
3
Foreign Countries: Reporting & Media Representation
3
Turkey: International Broadcasting, Public Diplomacy, Image Abroad
3
Journalists
3
Safety of Journalists: Law & Public Policies
3
Local Journalism
3
Local News
3
Media Assistance: Public Service Broadcasting
3
Interpersonal Communication, Interpersonal Relations
3
Media Literacy: Youth
3
Broadcasting Companies
3
Migrants
3
Right-Wing Extremism
3
Democracy
3
Governance & Accountability: Role of Media / Communication
3
Public & State Radios
3
Media Effects
3
Hinduism and Communication
3
Islamism
3
Judaism and Communication
3
Religious Television Programmes
3
Digital Television
3
Mobile Phones, Smartphones
3
Television Programmes & Genres
3
Youth and Media
3
Access to Media & Information
2
Civic Engagement, Citizen Participation, Civil Society & Media
2
Media Advocacy, Media Activism
2
Audience Feedback, Interaction & Participation
2
Book Reading Habits, Book Readers, Book Consumption
2
Internet & Social Media Use: Minorities
2
Elderly People: Media Use
2
Religious Media Use, Religious Media Audiences
2
History of Book Publishing
2
Muslim Book Publishing
2
Catholic Church
2
Children and Media
2
Children: Media Representation & Reporting
2
Children's Magazines
2
Media Literacy: Children
2
Coptic Orthodox Church
2
Christian Television
2
Arab Cinema, Middle Eastern Cinema
2
Educational Films & Videos
2
Videos
2
Digital Rights
2
Editorial Independence
2
Legal Threats to Media Freedom
2
Indirect Censorship, Soft Censorship
2
Killings of Journalists & Media Personnel
2
OSCE Representative of Freedom of the Media
2
Military: Communication Strategies & Practices
2
NGOs & Civil Society Organizations: Communication Strategies & Practices
2
Citizen Journalism, Community Journalism
2
Community Television
2
Traditional Communication
2
Oral Cultures & Traditions, Oral History, Oral Testimonies
2
Holocaust
2
Conflicts and Media
2
Conflicts & Wars: Roles of Digital Technologies & Conflict Narratives in Social Media
2
Dealing With the Past
2
Hate Speech Legislation & Regulation
2
Internet / ICTs and Conflicts
2
Peace Culture, Peace Education, Non-Violence
2
Media Monitoring, Media Observatories
2
Culture and Communication, Culture and Media
2
Creative & Cultural Industries
2
Cultural Heritage
2
Cultural Identity
2
Culture (General)
2
Fans, Fandom, Fan Cultures
2
Literature
2
Modernization Development Approaches, Developmentalism
2
Popular Cultures
2
Nonprofit Organizations, NGOs
2
Good Governance
2
Poverty Reduction: Role of Media
2
Rural Communication for Development
2
Street Television: Video Screenings in Public Places
2
Digital Inclusion
2
Electronic Commerce
2
Political Blogging
2
Online Magazines & Newspapers
2
Online Services
2
YouTube
2
News Websites & Portals
2
Digitalization, Digital Transformation
2
Digitalization, Environment & Sustainable Development
2
Online Learning, E-Learning
2
ICTs and Development
2
ICTs and Poverty Reduction
2
ICT Development Assistance
2
ICT Indicators
2
Diaspora Media
2
Ethnic Press, Minority Press
2
Racism in Social Media & Digital Communication
2
Disinformation & Misinformation Law & Regulation
2
Health Disinformation & Misinformation
2
Library Assistance (Development Cooperation)
2
Public Libraries
2
Entertainment Media Industries & Markets
2
Economic Conditions
2
Labour, Labour Markets, Labour Laws, Working Conditions
2
Educational Radio Programmes
2
Entertainment and Media / Communication
2
Gaming, Video Games
2
Sports Reporting
2
Television Dramas
2
Television Serials
2
Environmental Communication
2
Climate Change Communication, Climate Journalism
2
Media Assistance: Environmental Communication
2
Defamation, Libel, Slander
2
Bribery & Corruption in Journalism
2
Evaluation Methods, Evaluation Tools
2
Gender & Religious Communication
2
Gender Representation & Stereotypes in the Media
2
Health Campaigns: Experiences
2
Health Journalism
2
Colonial Legacies
2
History (General)
2
China: Transnational Information Operations, International Broadcasting, Public Diplomacy
2
Developing Countries Reporting & Representation in Foreign / International Media
2
International News Flow
2
Foreign Television Programmes
2
Globalisation of Media
2
Image Abroad
2
Influence of Media on Foreign & International Policies
2
Media Law & Regulation: International Standards & Practices
2
Regional (Transnational) Integration & Communication
2
Satellite Television
2
Transnational Media Corporations, International Media Companies
2
Foreign Policies
2
Council of Europe
2
OSCE
2
UNESCO
2
Media Assistance: Investigative Journalism
2
Journalism Concepts & Cultures
2
Journalism Education Curricula
2
Stringers & Fixers (Journalism)
2
Poverty & Impoverished People: Reporting & Media Representation
2
Science Journalism
2
Arabic Language
2
Media Assistance: Financial Sustainability & Management
2
Media Assistance: Media & Information Literacy
2
Communication Systems
2
Stereotypes in Media & Communication
2
Media Literacy: Curricula
2
Media Literacy Policies
2
'Comparing Media Systems' (Hallin/Mancini, 2004)
2
Media System Analyses & Typologies
2
Transition Countries: Media Systems & Media Landscapes
2
Human Rights
2
Television Law & Regulation
2
Failures, Mistakes, Shortcomings: Experiences & Learnings
2
Digital Media Use: Migrants & Diasporas
2
Photography
2
Documentary Photography
2
Accountability & Transparency
2
Political Communication
2
Radicalisation: Influence of Media
2
Public Opinion
2
Press
2
Public & State Television
2
Satellite Radios
2
Manipulation
2
Religion and Communication
2
Islam
2
Muslim Digital Media & Online Communities
2
Antisemitism
2
Religion and Politics
2
Religion and Society
2
Religious Discrimination, Persecution of / Violence Against Religious Groups
2
Religious Populism
2
Research in Media & Communication
2
Comparative Approaches & Methods in Communication Research
2
Rural Communication, Media in Rural Areas
2
Civil Society
2
COVID-19 Pandemic: Economic, Political and Social Effects
2
Ethnic Groups, Ethnic Minorities
2
Social Classes
2
Digital Switchover
2
Radio Broadcasting Equipment & Technologies
2
Television Transmitters
2
Telecommunication Industries & Markets
2
Regional Television
2
Postcolonial & Decolonial Communication Approaches
2
Urban Communication, Urban Media
2
Visual Communication
2
Youth Cultures, Youth Milieus, Youth Identities
2
Flow of Information
1
Open Data
1
Adblocking
1
Merchandising & Social Merchandising
1
Advocacy
1
Advocacy & Empowerment: Disadvantaged & Vulnerable Groups
1
Advocacy & Empowerment: Migrants & Refugees
1
Advocacy & Political Films
1
Celebrity Humanitarianism
1
Agriculture & ICTs, e-Agriculture
1
Geography
1
Film Audiences, Film Consumption
1
Health Information Access & Use
1
Information Needs
1
Information Needs & Media Use: Refugees & Displaced People
1
Media Diaries
1
Media Socialisation, Media Biographies, Media Life Journeys
1
Media Use: Children
1
Mobile Phone Use: Women
1
Television Use: Women
1
Print Media Use, Press Readers
1
Reading, Reading Habits, Reading Skills
1
Authoritarian Regimes: Transnational Repression
1
Book Publishing
1
Christian Book Publishing
1
Textbooks, Textbook Development, Publishing & Research
1
Transnational Book Trade, International Book Trade
1
Youth Literature & Books
1
Campaigning
1
Campaign Strategies
1
Information Campaigns
1
International Media Events
1
Radio Campaigns
1
Catholic Church and Communication
1
Catholic Church: Public Relations & Institutional Communication
1
Télé Lumière (Catholic Television Channel, Lebanon)
1
Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Oriental Catholic Churches
1
Benedict XVI (Pope)
1
Popes & Papacy: Media Representation & Communication Strategies
1
Child Protection, Protection of Minors
1
Children's Films
1
Children's Media
1
Children's Radio Programmes
1
Children's Television Programmes
1
Educational Comics & Comics for Development
1
Political Cartoons & Comics
1
Religious Contents & Meanings in Cartoons & Comics
1
Girls and Media
1
Media Reception & Effects: Children
1
Puppetry
1
Christian Communication
1
Christian Churches & Denominations
1
Adventist Church
1
Evangelical Churches
1
Sat-7 (Television Channel)
1
Televangelism
1
Homiletics, Preaching, Sermons
1
Sects
1
Aesthetics in Film & Visual Communication
1
Cinema in the Global South & Third Cinema
1
Development Education: Films
1
Film and Religion, Religion in Motion Pictures
1
Film Trade, Film Export & Import
1
Film Genres
1
Black & White Films
1
Ethnic Films, Minority Films
1
Ethnographic Films
1
Horror Films
1
Silent Films
1
Violence in the Media: Film
1
War & Political Violence in Cinema
1
Film Industries
1
Bollywood
1
Hollywood
1
Film Markets
1
History of Film & Cinema
1
Media Assistance: Film Funding
1
Screenwriting, Film Scriptwriting, TV Scriptwriting
1
Chilling Effects (Discouragement of Legitimate Exercise of Legal Rights)
1
Freedom of Expression Principles
1
Intellectual Property
1
Copyright Law
1
Plagiarism
1
Media Assistance: Freedom of Expression & Safety of Journalists
1
Internet Censorship Circumvention Tools & Strategies
1
United Nations Plan of Action on the Safety of Journalists and the Issue of Impunity
1
Communication Strategies
1
Crisis Communication
1
Government Propaganda
1
Government / State Advertising: Allocation Policies & Regulation
1
State News Agencies, Government News Agencies
1
Nonprofit Public Relations: Experiences
1
Press Releases & Press Conferences
1
Strategic Communication Planning
1
Community Development
1
Street Papers
1
Community Reporters, Media Volunteers
1
Community Telecommunication Networks
1
Graffiti, Wall Paintings, Street Art
1
Telecentres, Community Telecentres, Internet Cafés
1
Conflicts
1
Conflicts, Conflict Prevention & Management, Mediation, Peacebuilding
1
Conflicts: Victims' Perspectives
1
International Conflicts
1
Perpetrators
1
Religion and Justice / Peace / Reconciliation
1
Religion and Conflicts, Religious Conflicts, Religious Violence
1
Islamic State (Political-Religious Extremist Organization)
1
Civil Wars
1
Conflict-Sensitive Digital Technology Use & Social Media in Prevention & Transformation
1
Conflict-Sensitive Radio Journalism, Radio in Conflict Prevention & Transformation
1
Crime & Violence Reporting
1
Cyberwarfare, Cyber Operations: Attacking Enemy Computers, Software, and Control Systems
1
Early Warning: Conflicts & Crises
1
Extremist Recruitment through Media
1
Human Rights Protection & Violations: Media Representation & Reporting
1
Media Assistance: Conflict Prevention, Mediation & Reconciliation
1
Media Law & Regulation in Conflict Areas
1
Religious Communication in Conflicts & Peacebuilding
1
Trauma, Coping with Trauma, Trauma Therapy
1
War Propaganda, Propaganda in Conflicts
1
Discourse & Discourse Analysis
1
Rumours & Rumour Management
1
Digital Anthropology, Cyberanthropology
1
Architecture
1
Theatre
1
Street Theatre
1
Theatre for Development
1
Religious Art
1
Visual Arts, Painting
1
Cultural Diversity
1
Cultural Domination, Media Imperialism, Cultural & Media Dependency
1
Cultural Pluralism
1
Memes
1
Literature: Social Criticism
1
Narratives, Narrative Structures
1
Poetry
1
Religious Literature & Religious Motifs in Literature
1
Manuscripts, Scripture, Calligraphy
1
National Character
1
Popular Religious Cultures & Practices
1
Reading Promotion
1
Religion and Culture
1
Religious Music
1
Development Assistance
1
Donor Coordination, Funder Collaboration, Aid Harmonsation
1
Corporate Donors
1
United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
1
Open Society Foundations (NGO network)
1
Development Communication Projects: Case Studies
1
ICT / Internet Projects (Development Aid)
1
Sustainable Development Goals (SDG)
1
Communication for Local Development
1
Entertainment Education, Edutainment
1
Edutainment Campaigns: Concepts & Strategies
1
Edutainment Campaigns: Experiences
1
Edutainment Radio Programmes
1
Governance Support Communication
1
Digital Communication, Digital Media
1
Algorithms & Big Data
1
Cyberbullying, Cyberharassment
1
Data Governance, Data Justice, Data Sovereignty
1
Digital Businesses
1
Digital Entrepreneurs, Tech Entrepreneurs
1
Digital Healthcare & Information, Mobile Health, E-Health, Telemedicine
1
Digital Media, Internet & Religion
1
Digital Media Research, Digital Communication Research
1
Governance & Accountability: Role of Digital Communication
1
Hackers & Hacking
1
Internet and Development
1
Internet and Society / Social Change
1
Internet Business Management
1
Internet / ICTs and Social Change
1
Internet Shutdowns
1
Media Assistance: Digital Journalism & Social Media
1
Chat
1
Digital Market Concentration
1
Online Radio, Internet Radio, Radio Streaming
1
Podcasts
1
Netflix
1
Open Access Publishing
1
Blogging, Blogs
1
TikTok
1
Video & Foto Online Communities
1
Instagram
1
WhatsApp
1
Trolling (Social Media)
1
Websites
1
Ethnic / Minority Online Communities & Websites
1
Artificial Intelligence
1
Generative AI, including ChatGPT et al.
1
Information Society
1
Afro-Latin Americans, Afroamerican Population
1
Albinism
1
Ethnic Radios, Minority Radios
1
German-Language Media Abroad
1
Homeless People
1
Media Assistance: Minority Media
1
Minorities
1
Minorities & Disadvantaged Groups: Media Policies & Regulations
1
Minority Rights
1
Perceptions & Attitudes Towards Minorities
1
Religious Minorities & Media
1
Effects of Disinformation on Democracy
1
Identifying & Researching Disinformation
1
Media Literacy: Disinformation, Fake News, Hate Speech
1
Digital & Online Archives
1
Digital Economies & Markets
1
Economic Contribution of the Media Industries to GDP
1
Media Market Transparency
1
Press Markets
1
Radio Markets
1
Transnational Media Markets, International Media Markets
1
Media Ownership Regulation & Transparency
1
Nonprofit Journalism, Nonprofit Media
1
Television Economics
1
Small Enterprises, Micro Businesses, Small & Medium Enterprises (SME)
1
Religion and Economics
1
Audiovisual Media in Education
1
Civic Education: Use & Role of Media
1
Educational Television
1
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC)
1
Infotainment, Politainment
1
Climate, Climate Change, Climate Change Adaptation
1
Contamination, Pollution
1
Environmental Organizations
1
Environmental Protection
1
Defamation: Effects on Victims
1
Objectivity & Veracity of Reporting
1
Bias in News Media
1
Sexuality: Media Representation, Sexually Explicit Media Content, Pornography
1
Religious Communication Ethics, Religious Media Ethics
1
Sensationalist Journalism, Yellow Press
1
Development Projects: Evaluation, Monitoring, Impact Assessment
1
Evaluation in Conflict & Fragility Settings
1
Health Campaigns: Monitoring & Evaluation
1
Impact Assessment & Outcome Evaluation
1
Meta Evaluations, Cluster Evaluations
1
Most Significant Change (MSC)
1
Participatory, Collaborative & Empowerment Evaluation
1
Women (General)
1
Women's Organizations
1
Decolonial & Non-Western Approaches
1
Health Communication
1
Alcohol Abuse: Prevention & Media Representation
1
Health Campaigns: Message Design
1
Health Campaigns: Planning & Implementation
1
Health Radio Programmes
1
Colonial Period
1
Decolonisation & Independence (General)
1
First World War (1914-1918)
1
History of Media: Colonial Period
1
History of Photography
1
Local History & Memory
1
Nazism
1
Slavery, Slaves
1
Indigenous Communication
1
Ethnographic Photography
1
Indigenous Journalists & Communicators
1
Indigenous Media, Indigenous Language Media Productions
1
Indigenous Languages
1
Adaptation of Media Products to Other Countries / Cultural Contexts
1
Africa: Foreign Media Representation & Image Abroad
1
Foreign ICT & Telecommunication Investments & Ownership
1
Foreign Media Reception & Effects
1
Germany: Foreign Media Representation & Image Abroad
1
Globalisation: Impact on (Local) Media & Communication
1
Media Assistance: Transnational Exchange & Cooperation
1
Russia: Foreign Media Representation & Image Abroad
1
Transnational Television, International Television
1
Transnational Communication
1
Transnational & Comparative Communication Research
1
Transnational Journalism Cooperation & News Exchange
1
China: Foreign Policy, Foreign Investments, Development Assistance
1
NATO
1
United Nations (UN)
1
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
1
Awards & Prizes: Journalism Awards
1
Journalism Studies & Research
1
Exiled Journalists
1
Journalists: Trust in Public Institutions
1
Youth Journalists, Youth Correspondents, Youth Media Volunteers
1
Labour Market for Journalists
1
Mobile Journalism, Video Journalism
1
Television News
1
Photojournalism
1
Business & Economics Journalism
1
Corruption Reporting & Role of Media in Curbing Corruption
1
Forced Labour & Human Trafficking: Reporting & Media Representation
1
Political Reporting
1
Judaism: Media Representation & Reporting
1
Television Journalism
1
Abbreviations
1
Bilingualism, Multilingualism
1
Linguistic Diversity
1
Linguistic Diversity: Internet & Digital Media
1
Translations & Translating
1
Local Communication & Media
1
Local Press
1
Local Radios, Local Radio Programmes
1
China: Media Assistance
1
European Union: Media Assistance
1
Media Assistance: Donor Organizations
1
Media Assistance: Implementing Organizations
1
Deutsche Welle DW Akademie
1
Media Assistance: Interaction with Foreign Policies
1
Media Assistance: Law & Regulation, Media Policy Consultancies
1
Media Assistance: Lessons Learned
1
Media Assistance: Regional Approaches & Experiences
1
Media Assistance: Training Institutions
1
USA: Media Assistance
1
Business Communication
1
Communication Processes
1
Presentation of Information
1
Organizational Communication, Institutional Communication
1
Media Privatization
1
Media Literacy: Teacher Training
1
Social Media Landscapes
1
Confidential Sources, Whistleblowing, Protection of Journalists' Sources
1
Economic / Social / Cultural Rights
1
Frequency Allocation, Radio Frequency & Spectrum Management
1
Human Rights Protection
1
Law Enforcement, Litigations, Legal Practice, Case Law, Jurisdiction
1
Law & Regulation: Protection of Confidential Sources & Whistleblowers
1
Licensing of Media
1
Media Law & Regulation: Constitutional Law
1
Media Law & Regulation: Muslim Countries
1
Ombudsmen
1
Regulatory Bodies
1
Sharia, Fatwas
1
Truth & Reconciliation Commissions
1
Change & Process Management
1
Cost-Benefit-Analysis, Cost-Effectiveness, Efficiency
1
Financing Media: Customer Payments, Subscription Models, User-Based Financing
1
Financing Not-For-Profit & Community Media
1
Financing Press & Print Media
1
Financing Public Service Media
1
Crowdfunding
1
Media Companies, Media Corporations, Media Enterprises
1
Radio Free Europe
1
Voice of America
1
Forced Migration, Forced Displacement
1
Migration Prevention Information, Informing Potential Migrants
1
Migrants & Refugees: Tailor-Made Media Products & Information Services
1
Popular Music
1
People with Disabilities & Communication / Media
1
Deaf & Hard of Hearing People
1
Khashoggi, Jamal (1958-2018)
1
Ousmane, Sembene
1
Colonial Photography
1
Conflict & War Photography
1
Arab Spring (2010-2012)
1
Government Policies
1
Internal Politics
1
Polarization, Political Polarization
1
Political Change
1
Political Doctrines
1
Hindu Nationalism
1
Political Extremism
1
Socialism
1
Totalitarianism
1
Political Parties
1
Political Resistance
1
Political Systems
1
Fragile / Post-Conflict States
1
Public Administration
1
Agenda Setting
1
Election Monitoring
1
Framing
1
Political Parties: Communication Strategies
1
Haaretz (Newspaper, Israel)
1
Monitoring
1
Project Coordination
1
Project Impact, Project Effects, Project Effectiveness, Project Efficiency
1
Stakeholders, Stakeholder Analysis, Stakeholder Participation
1
Radio Programmes & Genres
1
Radio Debates, Radio Talk Shows, Call-In Radio Programmes
1
Religious Radio Programmes
1
Radio Stations
1
Cyberpsychology
1
Media Psychology, Communication Psychology
1
Persuasive Communication
1
Buddhism and Communication
1
Confucianism
1
COVID-19 Pandemic & Religion
1
Taliban
1
Hinduism
1
Images in Religion, Images of God
1
Interreligious Dialogue
1
Islamophobia
1
Islamic Cultures: Role of Media
1
Muslim Cinema & Film Representation of Islam
1
Muslim Television Broadcasting
1
Religion (General)
1
Religious History
1
Religious Movements
1
Religious Practice
1
Secularization & Atheism
1
Youth & Religious Communication
1
Communication & Media Indicators
1
Delphi Method
1
Participatory Action Research
1
Focus Groups & Group Discussions (Qualitative Research Method)
1
Internet & ICTs in Rural Areas
1
Social Conflicts, Social Problems
1
Coalition Building
1
Rohingya
1
Networks & Networking
1
Social Change
1
Revolutions
1
Social Sciences Research
1
Society & Media, Media Sociology
1
Traditional Society
1
Technologies, Information & Communication Technologies
1
Alternative Technologies
1
Blockchain Technologies
1
Informatics
1
Robots, Robotics
1
Satellite Communication & Information Services
1
Open Source Software
1
Software Security
1
Mobile Phone Apps
1
Remote Work, Teleworking, Working from Home
1
Telephone
1
Commercial Television
1
Television Programmes, Specific
1
Theories of Communication & Media
1
Illustrations, Pictures, Images
1
Infographics & Data Visualization
1
Visual Cultures
1
Visual Representations
1
Youth Activism, Youth Civic Engagement, Youth Political Interests, Youth Protests
1
Youth, Adolescents
1
Youth & Digital Media
1
Youth Television Programmes
1
Youth Media
1
Youth: Media Representation & Reporting
1
transcription
1
Language
Document type
Countries / Regions
Authors & Publishers
Media focus
Publication Years
Methods applied
Journals
Output Type
"While the Turkish media market looks diverse from the outside because of the large numbers of outlets, it is increasingly concentrated in terms of opinion. The Media Ownership Monitor Turkey, carried out with IPS Communication Foundation/ bianet between July and October 2016, shows that the governm
...
Kurdish Documentary Cinema in Turkey: The Politics and Aesthetics of Identity and Resistance
Newcastle-upon-Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing (2016), xii, 269 pp.
"Documentary film is proving to be a particularly complex tool for the Kurdish social and political existence, as Kurds lack the official tools of history-writing and cultural preservation that are categorically associated with the capacities of a state. By delving into Kurdish documentary films as
...
How the World Changed Social Media
London: UCL Press; University College London (2016), xxiv, 262 pp.
"The first book in Why We Post, a book series that investigates the findings of nine anthropologists who each spent 15 months living in communities across the world, including Brazil, Chile, China, England, India, Italy, Trinidad and Turkey. This book offers a comparative analysis summarising the re
...
Social Media in Southeast Turkey: Love, Kinship and Politics
London: UCL Press; University College London (2016), xi, 194 pp.
"This book presents an ethnographic study of social media in Mardin, a medium-sized town located in the Kurdish region of Turkey. The town is inhabited mainly by Sunni Muslim Arabs and Kurds, and has been transformed in recent years by urbanisation, neoliberalism and political events. Elisabetta Cos
...
Media Sustainability Index 2016: The Development of Sustainable Independent Media in Europe and EurAsia
Washington, DC: IREX (2016), xxii, 318 pp.
"The three countries that this year experienced a decrease in overall score—Belarus, Azerbaijan, and Kazakhstan—were ones last year that had showed small but unexpected increases. Last year’s Executive Summary indicated that such increases were unlikely to be part of a larger upward trend; pan
...
Thirty Rising Media Markets 2016
London: ZenithOptimedia (2016), 51 pp.
"The markets we do include are a very diverse bunch, from the very closed and politically tightly controlled such as Laos; through a large number of nations on the African continent which have seen a sudden improvement in digital infrastructure thanks to the landing of several new submarine intercon
...
Der Film Hara Harwaa Reihaby von Emma Chodzaa als Instrument der staatlichen Beeinflussung des kollektiven Gedächtnisses in Abchasien
Frankfurt, Oder: Europa-Universität Vidriana, Bachelor Thesis (2016), 53 pp.
"Die Fallanalyse hat gezeigt, dass eine Erzählung vom Krieg 1992-93 propagiert wird, die einer abchasischen Version des Narrationsschemas 'Die Vertreibung von fremden Feinden' entspricht. Ein zentrales Element der Erzählung ist zudem, so ergab die Interpretation, eine betont positive Darstellung d
...
Freedom on the Net 2016. Silencing the Messenger: Communication Apps Under Pressure
Top Insights
Washington, DC; New York: Freedom House (2016), 1021 pp.
"Internet freedom has declined for the sixth consecutive year, with more governments than ever before targeting social media and communication apps as a means of halting the rapid dissemination of information, particularly during antigovernment protests. Public-facing social media platforms like Fac
...
Medien in Kasachstan: Entwicklung, Zustand, Perspektiven
Osteuropa, volume 66, issue 11 (2016), pp. 181-195
"Seit der Unabhängigkeit 1991 ist in Kasachstan ein Mediensystem entstanden, das formal viele Gemeinsamkeiten mit den Mediensystemen in konsolidierten Demokratien aufweist. Die Verfassung garantiert Meinungs- und Pressefreiheit, auf dem Medienmarkt herrscht Vielfalt, das Internet gewinnt zulasten d
...
Syrian Refugee Journalists Leaving ... To Tell the Tale
Paris: Reporters Without Borders (2016), 16 pp.
"After the Syrian uprising morphed into an armed struggle, the Syrian government increasingly lost control over vast areas of territory. With the loss of State control, its imposed rule on media faded, enabling media to flourish in those areas. In territories it still controlled, its grip became eve
...
Digital News Report 2016
Oxford: Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism (2016), 109 pp.
"This year we have evidence of the growth of distributed (offsite) news consumption, a sharpening move to mobile and we can reveal the full extent of ad-blocking worldwide. These three trends in combination are putting further severe pressure on the business models of both traditional publishers and
...
State of Emergency in Turkey: The Impact on Freedom of the Media
London: Article 19 (2016), 23 pp.
Ethnic Media, Conflict, and the Nation-State: Kurdish Broadcasting in Turkey and Europe and Mediated Nationhood
Media, Culture & Society, volume 38, issue 5 (2016), pp. 738-754
"Drawing on fieldwork among Kurdish broadcasters in Turkey and Europe, this article shows how ethnic media mediate nationhood in a conflict context. Despite rising interest in the media-nationhood nexus, and the expansion of studies on ethnic media, little is known about ethnic media in conflicts in
...
Silencing Turkey’s Media: The Government’s Deepening Assault on Critical Journalism
Human Rights Watch (2016), 74 pp.
"Following the abortive July coup in Turkey, the government has accelerated and intensified a crackdown on independent media which had already been underway for more than a year. Under the state of emergency declared in the aftermath of the coup attempt, the government has closed down independent me
...
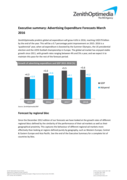
Executive Summary: Advertising Expenditure Forecasts March 2016
London: ZenithOptimedia (2016), 10 pp.
"ZenithOptimedia predicts global ad expenditure will grow 4.6% in 2016, reaching US$579 billion by the end of the year. This will be a 0.7 percentage point improvement on 2015: 2016 is a ‘quadrennial’ year, when ad expenditure is boosted by the Summer Olympics, the US presidential election and t
...
Elderly People's Choice of Media and Their Perceived State of Loneliness
Online Journal of Communication and Media Technologies, volume 6, issue 1 (2016), pp. 35-47
"This study aims at finding the relationship between elderly people’s perceived state of loneliness and their choice of (old and/or new) media instruments. The sample of the study consists of randomly selected 300 elderly people over 60 who reside in rest homes in two different cities, Hatay and �
...
Social Inequalities, Media, and Communication: Theory and Roots
Lanham et al.: Lexington Books (2016), xxxix, 272 pp.
The Praxis of Social Inequality in Media: A Global Perspective
Lanham et al.: Lexington Books (2016), xxiv, 269 pp.
" This volume contains chapters by an international array of scholars and provides case studies from various countries with critical empirical analysis of social inequalities and how they shape media narratives and experiences. The topics examined here include poverty in the media in Britain and Tur
...
Medien im Krieg - Krieg in den Medien
Wiesbaden: Springer VS (2016), ix, 404 pp.
"Das Thema Medien und Krieg wird in diesem Buch aus einer vierfachen Perspektive heraus behandelt. Es geht zum einen um die Frage nach der Berichterstattung über Kriege, zum zweiten um die Rolle von Medien im Krieg, drittens geht es darum, welche strukturellen Bedingungen von Krieg und Gesellschaft
...