Filter
152
Featured
Free Access
78
Key Guidance
2
Top Insights
9
Topics
Television Consumption, Televison Use, Television Audiences
34
Community Radios
17
Media Use, Media Consumption
15
Digital & Social Media Use, Internet Use
13
Trust in the Media, Credibility of Media
12
Radio
12
Print Media Use, Press Readers
11
History of Radio
11
Radio Programmes & Genres
11
Access to Media & Information
9
Media Use: Rural Populations
9
Mobile Phone Use
8
Rural Radio Programmes, Rural Radios, Rural Development & Radio
8
International Radio Broadcasting, Foreign Radio Broadcasting
8
Radio News
8
Advertising
7
Audiences & Users
7
Audience Feedback, Interaction & Participation
7
Local Radios, Local Radio Programmes
7
Radio Landscapes
7
Audience Research
6
Radio Markets
6
Radio Law & Regulation
6
Public & State Radios
6
Radio Programming, Programme Structures & Schedules
6
Radio Advertising
5
News Consumption & Information Sources of Media Users
5
Target Groups
5
Educational Radios
5
Media Assistance: Radio
5
Radio Stations
5
Rural Communication, Media in Rural Areas
5
Community Radio Audiences & Use
4
Film Audiences, Film Consumption
4
Media Use: Urban Populations
4
Media Use: Women, Female Media Audiences
4
Catholic Radios
4
Conflict-Sensitive Radio Journalism, Radio in Conflict Prevention & Transformation
4
Radio Culture
4
Radio for Development
4
Rural Communication for Development
4
Online Radio, Internet Radio, Radio Streaming
4
Podcasts
4
Media Landscapes, Media Systems, Media Situation in General
4
BBC
4
Radio Production
4
Digital Radio
4
Advertising Markets & Industries
3
Audience Clubs & Listener Groups
3
Audience Research Methods
3
Audience Research: Planning & Implementing Surveys
3
Audience Segmentation, User Typologies, Personas
3
Media Assistance Projects & Programs: Case Studies
3
Television Markets
3
Educational Radio Programmes
3
Gender and Radio
3
Health Radio Programmes
3
Indigenous Radio Broadcasting
3
Radio Music
3
Radio Formats
3
Radio Studies & Research
3
Regional Radios
3
Book Reading Habits, Book Readers, Book Consumption
2
Television Use: Children
2
Media Use: Foreign / International Media
2
Media Use: Migrants & Diasporas
2
Media Use: Youth
2
Milieus, Lifestyles
2
Music Consumption & Use
2
Children's Television Programmes
2
Media Freedom, Press Freedom
2
Participatory Communication
2
Traditional Communication
2
Digitalization, Digital Transformation
2
Media Markets
2
Radio Economics
2
Radio Schools
2
Training
2
Soap Operas & Telenovelas
2
Good Practice Examples
2
Radio Journalism
2
Communication Networks
2
Information
2
Civic Engagement, Citizen & Community Participation
2
Politics and Media
2
Watchdog Role of the Media
2
Public Media, State Media
2
Public Service Broadcasting
2
Cultural Radio Programmes
2
Radio Dramas, Radio Soap Operas, Radio Fiction
2
Youth Radio Programmes, Youth Radio Stations, School Radios
2
Radio Reception, Radio Psychology, Radio Effects
2
Commercial Radios
2
Kothmale Community Radio (Kothmale, Sri Lanka)
2
Radio Chaguarurco (Santa Isabel, Azuay, Ecuador)
2
Urban Radios
2
Radio Engineering & Technologies
2
Media Effects
2
Media Reception
2
Research in Media & Communication
2
Research Methods
2
Focus Groups & Group Discussions (Qualitative Research Method)
2
Access to Internet & Digital Communications
1
Advertising Audiences & Target Groups
1
Advertising Effects & Impact
1
Radio Spots
1
Agricultural Radio Programmes
1
Audience Composition
1
Audience Expectations & Satisfaction
1
Audience Letters
1
Audience Research in Media Assistance
1
Internet & Social Media Use: Minorities
1
Gaming: Uses & Effects
1
Health Information Access & Use
1
Information Needs
1
Information Needs & Media Use: Refugees & Displaced People
1
Interactive Radio: Audience Participation, Interaction & Feedback
1
Media & ICT Use in Authoritarian Regimes / Dictatorships
1
Media Use: Children
1
Media Use: Families
1
Media Use: Foreign & International News
1
Media Use: Minorities & Disadvantaged Groups
1
Mobile Phone Use: Minorities
1
Media Use: Preferred Contents & Programmes
1
Media Use: Public Service & State Media
1
Radio Use: Women
1
Mobile Phone Use: Youth
1
Opinion Polls, Public Opinion Research
1
Reading, Reading Habits, Reading Skills
1
Media Use: Catholic Media Productions
1
Book Publishing
1
Catholic Radio Programmes
1
Radio La Voz de la Selva (Iquitos, Peru)
1
Radio Marañón (Jaén, Perú)
1
Radio Onda Azul (Puno, Peru)
1
Radio Quillabamba (Quillabamba, Peru)
1
Radio Veritas (Johannesburg, South Africa)
1
Animated Cartoons, Animated Films
1
Christian Radios
1
Urban Pastoral
1
Cinema
1
Film Markets
1
Plagiarism
1
Media / Communication Control
1
Censorship Circumvention Tools & Strategies
1
Public Diplomacy, Cultural Diplomacy
1
International Organizations: Communication Strategies & Practices
1
Alternative Communication & Media
1
Alternative Radios
1
Comunicación Popular
1
Community Development
1
Community Participation in Community Media
1
Faith-Based Community Radios
1
Media Assistance: Community Radios
1
Media Assistance: Conflict Prevention, Mediation & Reconciliation
1
Media Assistance: Conflict-Sensitive & Peace Journalism
1
Violence in the Media: Reception & Effects
1
Contents of Media
1
Decoding
1
Media Quality
1
Arts
1
Theatre
1
Theatre Audiences
1
Popular Art, Folk Art, Handicrafts
1
Cultural Heritage
1
Cultural Identity
1
Cultural Studies
1
Culture (General)
1
Fans, Fandom, Fan Cultures
1
Museums
1
Popular Cultures
1
Development Journalism & Media Representation of Development Issues
1
Entertainment Education, Edutainment
1
Edutainment Radio Programmes
1
Online Communication
1
YouTube
1
Online Learning, E-Learning
1
Prisoners & Communication / Media
1
Media Literacy: Disinformation, Fake News, Hate Speech
1
Economics of Media
1
Economic Contribution of the Media Industries to GDP
1
Music Industries & Markets
1
Radio Industries
1
Press Markets
1
Media Ownership
1
Financing Radio
1
Adult Education
1
Interactive Audio Learning, Interactive Digital Learning, Interactive Radio Instruction
1
Media Assistance: Educational & Instructional Media
1
Entertainment and Media / Communication
1
Infotainment, Politainment
1
Leisure
1
Radio Entertainment
1
Sexuality: Media Representation, Sexually Explicit Media Content, Pornography
1
Sensationalist Journalism, Yellow Press
1
Rural Women & Communication
1
Malaria Communication
1
History of Television
1
Indigenous Languages
1
Perceptions & Attitudes Towards Indigenous Peoples
1
Image Abroad
1
Media in the Global South / Developing Countries
1
United Nations (UN)
1
Journalism
1
Journalistic Quality
1
News
1
News Reception
1
Business & Economics Journalism
1
Election Reporting
1
Bilingualism, Multilingualism
1
Local Television
1
COVID-19 Pandemic: Effects on Journalism, Media & Communication
1
Information Exchange
1
Media, Mass Media
1
Media & Communication Policies
1
Information Policies
1
Media & Information Literacy
1
Television Landscapes
1
Media Law & Regulation
1
Licensing of Media
1
Marketing & Branding
1
Quality Management
1
Radio Management
1
Radio Sawa
1
Migrants, Refugees, Diasporas & Media
1
Pop Music
1
People with Disabilities: Reporting & Media Representation
1
Centralization
1
Governance & Accountability as Focus of Radio Programmes
1
Media Capture, Vested Political & Other Interests in the Media
1
Opinion Leaders, Politicians, Decision Makers, Elites
1
Political Transition and Media
1
Public Spheres
1
Press
1
Project Impact, Project Effects, Project Effectiveness, Project Efficiency
1
Radio Magazines
1
Religious Radio Programmes
1
Muslim Radio Broadcasting
1
KKCR (Kagadi Kibaale Community Radio) (Uganda)
1
Radio Okapi (Democratic Republic of Congo)
1
University Radios
1
Emotions in Communication & Media
1
Media Psychology, Communication Psychology
1
Social Participation
1
Everyday Life
1
Uses-And-Gratifications Approach
1
Data Analysis & Interpretation
1
Qualitative Research Methods
1
Participatory Observation (Research Method)
1
Questionnaires, Questionnaire Design
1
Utilization & Implementation of Research Results, Research Reception & Effects
1
Rohingya
1
Social Control
1
Social Structure
1
Lower Classes
1
Upper Class
1
Technologies, Information & Communication Technologies
1
Short Wave Radio (SW)
1
Radio Sets, Radio Receivers
1
Television Sets
1
Television
1
Television Channels
1
Television Programming, Programme Structures & Programme Policies
1
Urban Communication, Urban Media
1
Suburbs, Poor Districts, Slums, Shanty Towns
1
Language
Document type
Countries / Regions
Authors & Publishers
Media focus
Publication Years
Methods applied
Journals
Output Type
Information Needs Assessment: Cox’s Bazar - Bangladesh
Arcata, Calif.; London: Internews (2017), 56 pp.
"There is no accessible media in the Rohingya language, leaving the Rohingya population of well over a million, now spread between Myanmar and Bangladesh, reliant on information only available in languages other than their own [...] This assessment, conducted in the Cox’s Bazar region of Banglades
...
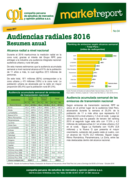
Audiencias radiales 2016: Resumen anual
Lima: CPI (2017), 8 pp.
Ethiopia TV & Radio Ratings 1st Jan – 30th April 2017
Kantar Media; Fojo Media Institute (2017), 50 slides
"KANA TV is the most popular station with over 30% share and an average audience of almost 3 million while EBS comes second reaching half the audience KANA TV reaches. EBC1, JTV, and Nahoo close out the top 5 stations which comprise 81% of total share." (Slide 9)
Audience Perceptions of Radio Stations and Journalists in the Great Lakes Region
Audiencia radial nacional rural: 83% de la población rural escucha radio
Lima: CPI (2016), 3 pp.
"El 83,1% de las personas de 11 a más años a nivel nacional rural escuchan radio por lo menos una vez a la semana y lo hacen principalmente a través de emisoras locales de FM y AM, alcanzando estas emisoras al 69,6% de la población rural con 12 horas en promedio de escucha semanal, este mayor al
...
"Este libro muestra los resultados de una investigación cuyo objetivo fue explorar la producción académica sobre Consumos Culturales en la Argentina en el período 2000-2012. Con el fin de poder delimitar el alcance del estudio, en un primer momento se definieron las dimensiones que esta indagaci
...
Audiencia radial de emisoras FM/AM: 15 principales ciudades [mayo]
Lima: CPI (2016), 1 p.
Audiencia radial de emisoras FM/AM: 15 principales ciudades [octubre]
Lima: CPI (2016), 1 p.
The Power of Publics: Competing Imaginaries of the Radio Audience in Kenya and Zambia
Cambridge: Centre of Governance and Human Rights, University of Cambridge (2016), 23 pp.
"With the liberalisation of the airwaves and the rising use of mobile phones since the 2000s, call- and text-in shows have become popular and lively features on broadcast media in Eastern Africa. Amidst expanding possibilities for listeners to speak and contribute to live radio broadcasts, new ways
...
Communication in Sierra Leone: An Analysis of Media and Mobile Audiences
London: BBC Media Action (2016), 52 pp.
"The survey indicates that radio remains the most widely accessed broadcast platform in Sierra Leone. In all, eight out of 10 (81%) Sierra Leoneans have access to radio, and 47% listen to it daily. Radio listenership is fractured, however, with no single station able to reach a national audience. Ar
...
"There are a sizeable number of people who have never had access to any form of media or device. Roughly one in three (34%) respondents have never had access to radio, television, newspapers, internet, or mobile phones. Furthermore, media is less accessible for women than it is for men. It is more c
...
Consumo radial y televisivo 2015
Lima: Consejo Consultivo de Radio y Televisión (CONCORTV) (2015), 18 pp.
Pesquisa brasileira de mídia 2014: Hábitos de consumo de mídia pela população brasileira
Brasília: Presidência da República. Secretaria de Comunicação Social (SECOM) (2014), 150 pp.
"A primeira edição da “Pesquisa Brasileira de Mídia” traz um retrato representativo e preciso sobre o uso que os brasileiros declaram fazer, atualmente, dos meios de comunicação social. Continua sendo predominante a presença da TV nos lares do País, apesar do rápido crescimento da intern
...
The Gambia Media Survey
Gates Malaria Partnership; Center for Innovation Against Malaria (2014), 56 pp.
"A national survey was completed in November 2004, designed to measure: media access and use; knowledge of Malaria, its prevention and cure; reach of the radio programme Bolongodala. The sample achieved represented the adult (15+) population of the Gambia estimated to be 768,200. Mandinka is the mos
...
85 años de la radiodifusión en Ecuador
Quito: CIESPAL (2014), 221 pp.
"Este libro propone un recorrido histórico y, al mismo tiempo, actual de la radio ecuatoriana, que va desde sus inicios en 1926, cuando hubo algunos experimentos de emisión de señales sonoras en varias provincias de Ecuador, hasta la radiodifusión por Internet. En ese itinerario, Hernán Yaguana
...
Community / Audience Survey Report Eastern Samar, Philippines: Summary of Key Findings with a Brief Analysis and Discussion
Internews (2014), 5 pp.
"The purpose of the survey was to understand the listenership and value of Radio Bakdaw, the information needs of the community and sources people would use to address specific information needs." (Page 1)
Participatory Media for a Non-Participating Community: Western Media for Southern Communities
International Communication Gazette, volume 76, issue 2 (2014), pp. 197-208
"This paper draws on the contrast between community media and the nature of its communities in Africa that are not participatory but use participatory media. The general contention is that participatory media in Africa preside over non-participatory communities. The paper uses data collected at one
...