Filter
2868
Featured
1676
157
24
Topics
200
154
152
141
68
65
64
63
59
56
55
50
49
49
47
46
45
42
40
39
39
39
38
38
37
37
37
37
37
36
35
35
34
34
34
34
34
34
33
33
32
32
32
32
31
31
31
31
31
30
30
29
29
29
29
28
28
28
27
27
27
27
26
26
26
26
25
25
25
24
24
24
23
23
23
23
23
22
22
22
22
22
22
21
21
21
21
21
21
21
21
21
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
19
19
19
19
19
19
19
19
19
19
19
19
18
18
18
18
18
18
17
17
17
17
17
17
17
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Language
Document type
396
370
133
118
98
66
43
37
23
22
21
21
13
13
9
9
7
6
6
6
5
4
3
3
3
2
2
1
1
1
1
Countries / Regions
Authors & Publishers
Media focus
Publication Years
Methods applied
Journals
Output Type
Food Security Communication: An Investigation Into the Influence of Radio Programmes on Irish Potato Farming in Nakuru County, Kenya
Journal of Development and Communication Studies, volume 8, issue 2 (2021), 11 pp.
"The Government of Kenya recognizes Irish potato as one of the food security and nutrition crops together with maize and rice (GoK, 2017). This study sought to investigate the influence of radio programmes in promoting Irish potato farming as a contributor to food security in Nakuru County. The stud
...
How the COVID-19 Fight Has Hurt Digital Rights in East Africa
Kampala: CIPESA (2021), 12 pp.
Sexual Harassment in the Media: Africa Report
Paris: World Association of News Publishers (WAN-IFRA) (2021), 51 pp.
"Almost half of women respondents had been sexually harassed at work (47%). Women were twice as likely to experience sexual harassment at work than men. For one in two women, the harassment was verbal (56%), and for one in three, it was physical (38%). Only 30% of cases of sexual harassment were eve
...
"Das Werk bietet, nach Ländern bzw. Regionen aufgeschlüsselt, einen kompakten und aktuellen Überblick über geschichtliche Herkunft, weitere Entwicklungen und aktuelle Herausforderungen der afrikanischen Kirche aus katholischer Sicht. Dabei liegt ein Akzent auf den Beziehungen der Ortskirche zu a
...
The Stepping Into Visibility Model: Reflecting on Consequences of Social Media Visibility – a Global South Perspective
Information, Communication & Society, volume 26, issue 2 (2021), pp. 405-424
"This article discusses activists’ need to reflect on how achieving social media visibility might translate into vulnerability. In order to provide activists with a tool for this reflection, the Stepping into Visibility Model has been developed and applied to two case studies: (a) an activist grou
...
Media Viability in East Africa: Tanzania
Aga Khan University; Deutsche Welle DW Akademie (2021), vii, 33 pp.
Media Development in Practice: Innovation for Dialogue. New Approaches and Innovative Solutions to Improve Public Dialogue in the Digital Era
Bonn: Deutsche Welle DW Akademie (2021), 26 pp.
"In Moldova, a series of hackathons led to the development of tech-based solutions to misinformation. In Ecuador, indigenous groups wrote their own stories on Wikipedia to strengthen their culture's representation and publicly correct misinformation. In Uganda, citizen journalists established a netw
...
African Media Barometer: South Africa 2021
Windhoek: Friedrich-Ebert-Stiftung (FES) (2021), 54 pp.
"Since its adoption on 1 July 2020, the Protection of Personal Information Act has bolstered freedom of expression and the right to privacy. This legislation aims to protect citizens’ personal information and balance the right to privacy with other rights, such as access to information. In Februar
...
Assessing the Barriers to Accessing ICT by People with Disability in Uganda
Kampala: CIPESA (2021), 16 pp.
Entertainment-Education Behind the Scenes: Case Studies for Theory and Practice
Deep Insights
Cham: Palgrave Macmillan (2021), xxxiii, 354 pp.
"This book lays out the history of entertainment-education and discusses the boundaries of what counts as entertainment-education and narrative persuasion, includes both authors who work within academia and authors who are practitioners, and chapters focusing on developed and developing countries; d
...
A Portrait of Ugandan Journalists in Turbulent Times: A Survey Report
Kampala: African Centre for Media Excellence (ACME) (2021), v, 45 pp.
Visual and Cultural Identity Constructs of Global Youth and Young Adults: Situated, Embodied and Performed Ways of Being, Engaging and Belonging
London; New York: Routledge (2021), 293 pp.
"Embracing an international perspective encompassing the Global North and Global South, chapters explore expressions and performances of youth and young adults as shifting and entangled, in and through the clothed body, gender, sexuality, race, artistic and pedagogical making practices, in spaces an
...
China's Projection of Soft Power in Terms of Constructive Journalism: A Media Content Analysis of Constructive News Coverage of South Africa by China Daily and South China Morning Post in 2015 and 2018
Transcience, volume 12, issue 1 (2021), pp. 24-43
"China is an increasingly major player in the latest global economic configuration. As a formerly developing nation, China has the potential to view the world through a lens distinctive from current Western hegemonies in its news media and soft power strategies. China has already invested heavily in
...
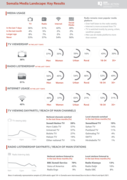
Somalia Media Landscape: Key Results
London: BBC Media Action (2021), 1 p.
"Radio remains most popular media platform. Over half listen to the radio weekly. Internet is more accessed than TV. TV is watched mostly by young, urban, wealthier people. Men use all media platforms more than women [...] A nationally representative sample of 2,004 adults aged 18+ in Somalia were i
...
"This Information Ecosystem Assessment documents how information around the COVID-19 pandemic is produced, consumed, and shared in Sudan contributing to the existence of multiple and overlapping information sub-systems within the supply side of the broader ecosystem. The findings show how the centra
...
"This report has documented the surveillance measures and practices in Kenya and Uganda during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The key trends include poor oversight over COVID-19 data collection, the lack of independent data protection authorities, the use of telecommunications data to ‘t
...
Fake News Misinformation and Hate Speech in Ethiopia: A Vulnerability Assessment
Brussels: European Institute of Peace (2021), 22 pp.
"The assessment found that Ethiopia's media ecosystem's weaknesses have made it vulnerable to fake news, misinformation, and hate speech. Some of the driving factors are undoubtedly historical, including the weak state of private media in Ethiopia, the critical role of the Ethiopian diaspora in medi
...