Filter
1208
Featured
513
29
13
Topics
114
109
99
75
68
67
64
63
62
61
59
58
53
51
49
41
39
37
35
35
34
34
32
31
30
29
29
29
28
27
25
25
24
24
24
23
23
22
21
21
20
20
20
19
19
19
18
18
18
18
18
17
17
16
16
16
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
14
14
14
14
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Language
Document type
48
33
32
29
24
21
20
16
9
5
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
Countries / Regions
Authors & Publishers
Media focus
Publication Years
Methods applied
Journals
Output Type
Analysis of Peruvian Newspaper Portrayal of Chinese Foreign Direct Investments From 2001 to 2020: An Exploration of Factors Influencing International Economic News Reporting
International Journal of Communication, volume 18 (2024), pp. 2598-2625
"In recent years, the economic exchanges between China and Latin American countries have been further deepened, and news about Chinese foreign direct investments (FDIs) in the region responds to economic reality and the different stages of changing international relations and media characteristics.
...
Russian Public-Diplomacy Efforts to Influence Neighbors: Media Messaging Supports Hard-Power Projection in Ukraine and Georgia
International Journal of Communication, volume 18 (2024), pp. 2661-2684
"Nations use media to disseminate stories about their culture, history, and values. This study explored Russian public-diplomacy efforts by examining news content exported to its neighbors, Ukraine and Georgia, from February 2021 to July 2021, approximately one year before Russia’s invasion of Ukr
...
Unearned prestige: How The Economist covers the war in Ukraine
Media Development, issue 4 (2024), pp. 24-30
"The newspaper’s sense of what the story is about influences who is considered qualified and appropriate to quote. Conversely, quotes are blocks that build and legitimize the narrative; they are all the more important in a journal, like The Economist (TE), not known for doing investigative journal
...
Chinese Media Engagement with Africa and the Role of African Agency: The Cases of Kenya and Ethiopia
"This policy brief reveals the complexity of Chinese media engagement with African countries, highlighting involvement from both state and private actors through a variety of forms. At its core, China aims to champion its development paradigm as a viable alternative to Western models, augment its so
...
Bound by Exile: Exploring Kinship Dynamics and Role Perceptions among Diaspora Journalists
Journalism Studies (2024), 20 pp.
"The escalating dangers journalists face globally have led to a marked increase in media professionals seeking safety away from their home countries. As a result, journalists are increasingly forced to choose between silence and survival, with many opting for the latter in the form of diaspora reloc
...
Historical Media Memories of the Rwandan Genocide: Documentaries, Films, and Television News
Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press (2024), xii, 297 pp.
"The Rwandan genocide is the second most audio-visually recreated genocide after the Holocaust, with approximately 200 films and documentaries produced in 39 countries between 1994 and 2021. Historical Media Memories of the Rwandan Genocide studies the construction, the development, and the recreati
...
Capturing News, Capturing Democracy: Trump and the Voice of America
New York: Oxford University Press (2024), viii, 294 pp.
"How did the Trump administration capture one of the world’s most important public service news networks? This book uses rare interviews and an analysis of private correspondence and internal documents to explain why and how Voice of America (VOA) became intensely politicized from 2020 to 2021. It
...
La couverture médiatique des soulèvements iraniens 2022-2023 : Analyse de la presse française
Paris: L'Harmattan (2024), 179 pp.
"En septembre 2022, suite à l'assassinat d'une jeune fille kurde iranienne par les patrouilles d'orientation, l'Iran connaît des mois de soulèvements contre le régime. Si ces derniers adoptent de nouvelles formes de contestation, ils sont causés par les mêmes injustices que les précédents mo
...
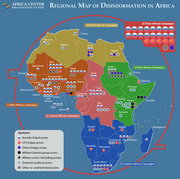
Mapping a Surge of Disinformation in Africa
Washington, DC: Africa Center for Strategic Studies, March 13 (2024)
"Disinformation campaigns have targeted every region of the continent. At least 39 African countries have been the target of a specific disinformation campaign. Disinformation tends to be concentrated. Half of the countries subjected to disinformation (20 of the 39) have been targeted three or more
...
Der russische Angriffskrieg gegen die Ukraine in den deutschen Medien: Kritik des Maßstabs „ausgewogene Bewertung“ in Inhaltsanalysen
Publizistik, volume 69 (2024), pp. 455-493
"Inhaltsanalysen über die Darstellung von Konflikten in den Medien werden häufig durchgeführt, um den Vorwurf der Einseitigkeit empirisch zu überprüfen. Dies wirft die normative Frage auf, wie die Forderung nach einer ausgewogenen Bewertung, d. h. einer Gleichverteilung positiver und negativer
...
K-Pop Fandom and Political Activism in Thailand’s 2020 Student Uprising
International Journal of Communication, volume 18 (2024), pp. 5296-5320
"Korean popular culture has taken the world by storm with the recent rise of Korean entertainment globally, such as Squid Game on Netflix and the Oscar Award-winning Parasite. Fans of Korean popular culture have formed coalitions in Asia, North and SouthAmerica, and other parts of the world. These c
...
Two Years On: An Analysis of Russian State and Pro-Kremlin Information Warfare in the Context of the Invasion of Ukraine
London: Institute for Strategic Dialogue (ISD) (2024), 25 pp.
"This report provides an overview of how Russian state and pro-Kremlin propaganda undermining international support for Ukraine has evolved over the two years since the beginning of the full-scale invasion on 24 February 2022. It outlines a range of semi-covert tactics through which Russian state an
...
Structuring Exiled Journalism in a More Authoritarian World
Mediation: Biannual Publication of Fondation Hirondelle, issue 13 (2024), 6 pp.
"Hundreds of endangered journalists living in authoritarian or conflict countries are forced into exile each year. And the phenomenon is growing. How can we organize collectively to protect them, help them recover and keep on doing their job from the host country?" (Page 1)
"As press freedoms around the globe erode, journalists are building networks outsidetheir home countries to continue reporting." (Summary)
China's Discourse Power: Capabilities and Impact
Washington, DC: Atlantic Council (2023), 40 pp.
Mundo China: The media partnership reframing China’s image in Brazil
International Communication Gazette, volume 85, issue 1 (2023), pp. 63-79
"This paper explores China’s increasing media engagement with Latin American partners. It examines the case of Mundo China (MC), a China-news segment broadcast by the Brazilian news channel BandNews TV and co-produced in partnership with CCTV. By conducting content analysis, we assess how China is
...
Breaking the Silence: The 10 Most Under-Reported Humanitarian Crises of 2022
London: Care International (2023), 28 pp.
"Our 2022 report shows that all of the most under-reported crises are now in Africa. Hunger is rampant and spreading, particularly in East Africa where one of the worst droughts in living memory is causing over 21 million people to face life-threatening hunger. Water becomes scarcer every day, crops
...