Filter
1795
Featured
937
44
13
Topics
212
191
191
122
119
106
96
96
88
86
84
76
74
68
68
65
64
61
53
53
50
50
49
47
44
44
44
41
41
39
38
36
36
35
34
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
28
28
27
27
26
26
26
25
25
25
25
25
25
24
24
23
23
23
22
22
22
21
21
20
20
19
19
18
18
18
17
17
17
17
16
16
16
16
16
15
15
15
15
15
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Language
Document type
120
116
111
85
27
24
19
18
12
8
5
5
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
Countries / Regions
Authors & Publishers
Media focus
Publication Years
Methods applied
Journals
Output Type
Media Propaganda and Human Rights Issues: What Can be Learnt from the Former Yugoslavia’s Experience in Relation to the Current Developments in the Arab Spring Countries?
Journal of Arab & Muslim Media Research, volume 8, issue 1 (2015), pp. 21-36
"Recent history has proven that media propaganda can impact severely on human rights issues. This article aims at exploring what can be learnt from previous lessons in order to avoid the same mistakes happening again and/or to fight them more efficiently. It questions the experience of the former Yu
...
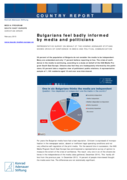
Bulgarians Feel Badly Informed by Media and Politicians
Sofia: Konrad-Adenauer-Stiftung (KAS), Media Program South East Europe (2015), 4 pp.
"59 percent of the population of Bulgaria do not consider the media to be independent. Many are undecided and only 17 percent believe reporting is free. The crisis of confidence in the media is continuing, according to a study on behalf of the KAS Media Program South East Europe. Citizens also feel
...
Media Guidelines for Reporting on Accessible Elections
General Election Network for Disability Access (AGENDA) (2015), 55 pp.
"For the last couple of years, there were more reporting on disability in the media but most of them only reporting and portraying the ‘uniqueness’ of disability. In the election news reporting, media only portray the Persons with Disabilities on the voting process but the news still did not hav
...
Les radios communautaires en Afrique de l'Ouest: Moteur de la gouvernance démocratique locale
In: Médias d'Afrique: Vingt-cinq années de pluralisme de l'information (1990-2015)
Paris: Karthala (2015), pp. 81-99
"L'article examine en particulier la relation entre les radios dites communautaires et la gouvernance locale. Se fondant sur l'exemple du Sénégal, elle montre comment la décentralisation politique et administrative d'une part et l'émergence des radios locales d'autre part ont été deux dynamiqu
...
Arab Media Moguls
London; New York: Tauris (2015), xiii, 233 pp.
"Transformations in the Arab media landscape are a key element in the regional dynamics of political change. Where do the private owners of Arab media outlets stand on the scene? What part, if any, have they played in weakening dictatorships, countering sectarianism and political polarisation, and r
...
Studying Political Microblogging: Parliamentary Candidates on Twitter During the February 2012 Election in Kuwait
International Journal of Communication, volume 9 (2015), pp. 2933-2953
"Kuwait boasts high levels of political and media freedoms compared to many countries in the Middle East, and it enjoys a vibrant social media scene. The Kuwaiti parliamentary election in February 2012 was the first election in which candidates widely utilized Twitter during their campaigns. This ar
...
Patronage, Politics and Performance: Radio Call-In Programmes and the Myth of Accountability
Third World Quarterly, volume 36, issue 8 (2015), pp. 1510-1526
"Assumptions about the role of call-in programmes as open spaces for pubic engagement and accountability often fail to account for the influence of existing power structures and multiple publics engaging in these programmes for a variety of reasons. Furthermore, the history of call-in programmes rev
...
Uchaguzi: A Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of ICTs, Statebuilding, and Peacebuilding in Kenya
Philadelphia: Annenberg School for Communication, Center for Global Communication Studies (CGCS) (2015), 43 pp.
"This study has found that Uchaguzi represents a blended model incorporating both crowd-seeding (placing monitors on the ground to collect data) and crowd-sourcing (collecting information from the public). The success of crowd-seeding is a function of Uchaguzi’s partnerships with local and interna
...
Humanitarianism 2.0
Humanitarianism 2.0 Project (2015), 102 pp.
"The five reports that make up this collection are variously concerned with humanitarian aid, social and cultural evolution, crisis response, the mitigation of cultural divides, and political unrest. The themes that bind them are an international movement towards public safety; a trust-based relatio
...
Kenya Decides: Kiswahili, Social Media and Politics in Kenya’s 2013 General Elections
Journal of African Media Studies, volume 7, issue 2 (2015), pp. 165-183
"In contrast to most recent studies focusing on how ICT and new media were catalysts for the 2007/08 post-election violence, this article will shed light on the role of Kiswahili and social media in the process of fostering participation in the 2013 general election campaigns. It takes a closer look
...
State-Media Financial Relations in Albania: Nurturing Client-Based Media Practices
Ljubljana: Peace Institute; South East European Media Observatory (2015), 19 pp.
"The transparency of media market in Albania continues to be low, including both commercial operations and the state funding, despite of the existing databases. The involvement of new actors, such as advertising agencies, and sister companies of media outlets, makes it even more difficult to track s
...
Towards a Political Economy of Communication in Development?
Nordicom Review, volume 36, issue Special Issue (2015), pp. 11-24
"In the development communication equation, whether more theoretical, empirical and analytical attention is given to ‘development’ or to ‘communication’ makes a difference: where the emphasis is on development, it is at the expense of communication. Since communication and media arguably pla
...
Effects of the Internet on Participation: Study of a Public Policy Referendum in Brazil
World Bank Group, Governance Global Practice Group (2015), 36 pp.
"Does online voting mobilize citizens who otherwise would not participate? During the annual participatory budgeting vote in the southern state of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil—the world’s largest—Internet voters were asked whether they would have participated had there not been an online voting
...
Die Entfaltung der E-Demokratie
"Die Entfaltung der E-Demokratie legt die Probleme der demokratischen Praxis in Südkorea offen: da sich die Bürger durch die politischen Institutionen nicht repräsentiert fühlen, suchen sie neue Wege, ihre Meinung zu äußern. Dabei sind die Netizens den politischen Akteuren und staatlichen Stel
...
Medien als Akteure in der politischen Transition: Bolivien im Autonomiekonflikt
Baden-Baden: Nomos (2015), 422 pp.
"Mechachal is a collaborative project developed by the University of Oxford and Addis Ababa University to understand the nature and potential of online debates in Ethiopia. Mechachal can be translated from Amharic as “tolerance”, or as one’s awareness of their own social sphere and willingness
...
#newactors, #oldproblems: How the Digital Sphere is Changing the Information Process and the Media Landscape in Africa
KAS International Reports, volume 31, issue 8 (2015), pp. 6-20
"Blogs and online content contribute significantly to opinion diversity in Africa today. Because of that, they are increasingly monitored by federal agencies, which aim to more strictly define the grey zone between journalism, blog-writing and opinion stating in social media. It is especially agains
...
Moderation from Bias: A Field Experiment on Partisan Media in a New Democracy
Journal of Politics, volume 77, issue 2 (2015), pp. 575-587
"Partisan media are often blamed for polarization in newly liberalized regimes. However, there is little empirical work on the subject, and information-processing theories suggest that extreme position taking is only one possible response to opinionated news. Rather, we theorize that partisan media
...
After the Revolution: Libyan and Tunisian Media Through the People’s Eyes
London: BBC Media Action (2015), 60 pp.
"Libya’s contested and, at times, chaotic political scene is reflected in its media, which represents a range of political and vested interests, sparking narrative and counter narrative. Ultimately, it has left people frustrated that they cannot access the information that they need. In Tunisia, t
...